Working with Max
In this recipe we will explore how to use soundworks in the Max (Cycling '74) environment and learn why we need to keep some specific workaround in mind in order to make our applications fully working and stable.
In the Working with Node Clients tutorial, we already explored the possibilities to work outside Web Browsers using Node.js, which to use soundworks in a large set of use (for example, using the node.script object exposed by the Max environment).
To illustrate this specific usage, we will create a simple soundworks-max application using the soundworks wizard that will be your base skeleton for your own projects!
Prerequisites
Related documentation
General structure
To illustrate such usage, while keeping things organized, we will structure our application as follow:
my-super-app
├── working-with-max # directory in which the soundworks application lives
└── my-max-patches # directory in which the Max patches livesKeep in mind that such structure is not mandatory, but a structure that may should be close to a "real-world" use case.
Scaffolding the application
First, open a terminal and go to your projects directory:
cd path/to/your/projects/folderCreate your top level application directory and go into it:
mkdir my-super-app
cd my-super-appAs seen in other tutorials, we will use the soundworks wizard to scaffold the application.
npx @soundworks/create@latest working-with-maxWhen the wizard asks you for plugins and libraries, just skip steps using enter.
Then, we will create a client (as well as his associated patch) using the template specifically adapted to the Max environment. When the wizard asks you for the configuration of the default client:
- Name it
helloworld - Select the
nodetarget - Select the
maxtemplate
# Create client
✔ Name of your new client (lowercase, no-space): … helloworld
✔ Which runtime for your client? › node
✔ Which template would you like to use? › max (`node.script`)
- Creating client "helloworld" in file "src/clients/helloworld.js"
- name: helloworld
- runtime: node
- template: max
? Confirm? › no / yesAfter confirming, the wizard will then ask you to inform where you would like to create your associated Max patch.
Where should we create your Max patch? (leave blank to use current directory) › ../my-max-patchesImportant Note
Since the wizard runs inside the soundworks application you are creating (in our example, in the my-super-app/working-with-max/ directory), the path you write here should be either an absolute path or a relative path from the soundworks application directory.
You can then exit the wizard :
? What do you want to do? › - Use arrow-keys. Return to submit.
create a new soundworks client
install / uninstall soundworks plugins
install / uninstall related libs
find documentation about plugins and related libs
get config information about you application
create a new environment config file
eject the launcher and default views from `@soundworks/helpers
check and update your dependencies
upgrade config files from JSON to YAML
❯ → exitRunning the application
To make sure the application is correctly set up, just go into the soundworks project directory and run the server in development mode:
cd working-with-max
npm run devThen, open the patch (my-max-patches/node-helloworld.maxpat) and click on the script start message box. You should see the Node for Max debug tool turning green with process running message. If you click on the hello message box, the object should answer world.
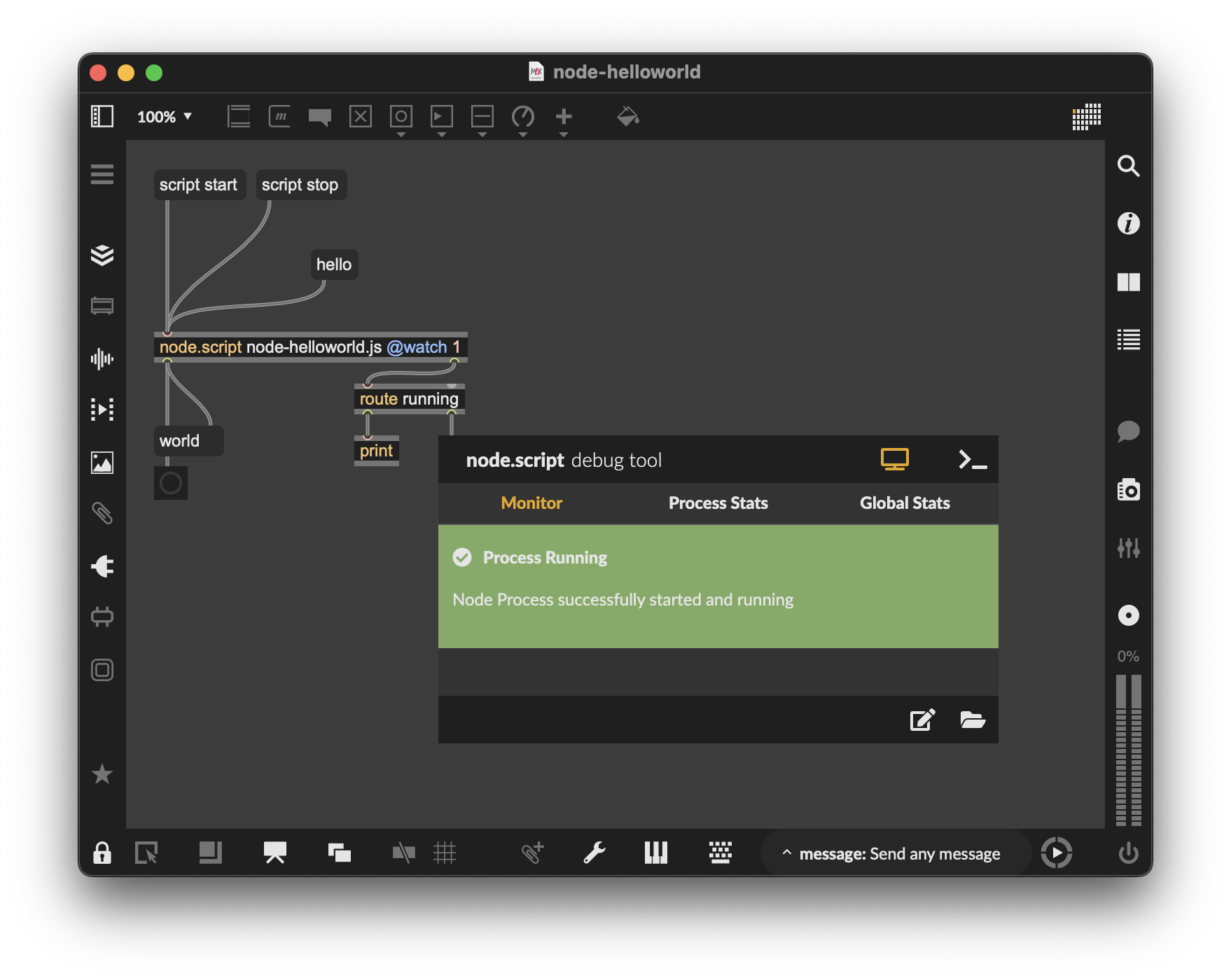
Tada! You have a fully working soundworks app with a client running in Node for Max!
How it works
Let's now have a closer look at your project's architecture and what was created by the wizard :
my-super-app
├── working-with-max # Soundworks directory (where you do soundworks stuff)
│ ├── src
│ └── clients
│ └── helloworld.js # Your client script (the one you edit)
│ ├── public
│ ├── node_modules
│ └── config
├── my-max-patches # Max directory (where you do Max stuff)
│ ├── node-helloworld.maxpat # A patcher skeleton with a node.script object
│ └── node-helloworld.js # The script used in your Max patch acting as a 'bridge'
# to the soundworks app (should remain unchanged)This architecture is meant to work around some inconsistencies on how the filesystem is handled between Node.js and Max. Indeed, if you take a closer look at the node.script object in the Max documentation, you will see that :
"Node and Max can sometimes disagree about how folder should be organized"
For that matter, the script instantiated by the node.script Max object should always remain in the same directory as your patch.
This lead to a conflict between the soundworks file structure, the need for the Node.js process to run within the my-super-app/working-with-max directory, and the need to organize your Max patches within your own workflow.
Solving these different conflicts and requirements leds us to create this "bridge / proxy" script (i.e. /my-super-app/my-max-patches/node-helloworld.js) which is responsible to configure the Node.js process to run in the right directory (i.e. my-super-app/working-with-max) and to import the "real" client script (i.e. /my-super-app/working-with-max/src/client/helloworld.js):
// change process current working directory to the soundworks application root
process.chdir('../working-with-max');
// import the "real" client source file
import('../working-with-max/src/clients/helloworld.js');Important notes
Moving you patches around
If for some reason you would like to move the patches and
jsscripts elsewhere, it is essential to keep in mind that you will also have to change the relative path to the soundworks app inside the associated proxy script (node-helloworld.js).The patch and its related proxy script should always together in the same directory.
A good practice could also be for example to have the entire directory in your File Preferences path in Max in order to use this patch as an abstraction.
Specificities of the soundworks client for Max
Compared to a regular Node.js client, the Node.js for Max as the following peculiarities:
- Import to use the
max-apiin node
import Max from 'max-api';Note that this will make the process to crash if run outside the Max node.script object.
- Hardcoded
ENVvariable to be able to switch between different environment configurations
const ENV = 'default';This is due the impossibility to define environment variables from the node.script object
